The Bitmap can be imported in two different ways.
| • | Normal Editable Bitmap Object |
| • | Draft Object with External Reference |

It is important to understand the difference because using it correctly gives you a big advantage and ability to create large photo-montages and collages without any slow down.
During export and Fine Print of a Normal Image its own internal data are used. So if we import a nice sharp 10 megapixel image, but resize and crop it to a 300x300 pixel image, this resized data quality will be what we get in export. This is fine for normal web graphics and other normal screen-resolution jobs as long as we don't want to use Megarender to export or print image larger than the document size.
Draft with External Reference uses the resized data only during designing to show it on canvas for easy manipulation, but during Export and Fine Print those data will be replaced with the original "best quality" data from the image on the disk. This makes big difference in Fine print and Megarender, but for normal screen-resolution graphic this gives very little benefit.
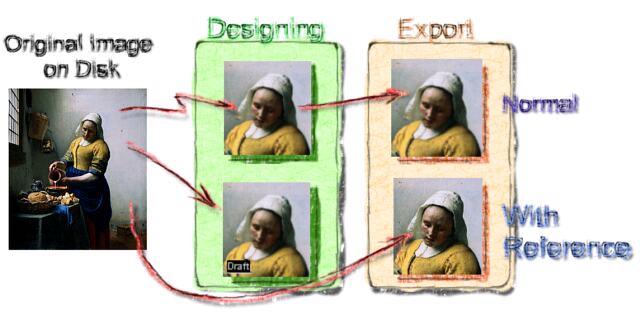
As we see on the graph above both Normal and Draft with Reference comes originally from a file. They both remember the link to the original file, but in Normal Image this is only used so we can re-crop the image later or during Update from Reference command. All the editing goes to the resized image in the memory.
In the Draft image the link goes much deeper. The image we see on canvas is only a shadow "placeholder" for the real data on the disk. When we do export those real data will be used.
Draft with External Reference image is therefore as close to resolution independent as a bitmap goes. We don't have to think in advance how large we need our document because no matter how large we export it - the best resolution will be always automatically used on the final output.
Note: During Export to file we still see the draft images displayed in the Export Preview but once we hit the final Export button the images will be then loaded from their Reference and the file rendered to disk.
When to use what
When you work on: |
You use: |
Why: |
Screen sized images/web graphics |
Normal Image |
If we are making screen-size graphics, for web for example, then we can simply import bitmap as Normal Image because our output will be equal or smaller than what we design on the screen. There will be no benefit in using Draft and we don't have to take care of the external references. |
Photo Collages or posters for large export or print |
Draft with External Reference |
If we are making a photo collage for print or for large export then using Draft with External Reference will give us a huge benefit of automatically using the right amount of resolution for any size of the output. For such project we expect to use Megarender or Fine Print which multiply the size of the canvas. So we design small for fast manipulation and then export big without loss of quality. |
Copy of the Reference, REF file.
When we try to use a bitmap-only effect on the Draft Image (such as painting over it or using some bitmap-only effects like contrast or levels) we will be prompted to create a copy of the Reference. Since the Draft is a placeholder for the real data on the disk, our changes have to go somewhere. Because we don't want to modify the original Reference image, we need to create a copy of it and then modify the copy. The new file will have extension *.ref and all the changes or any link to Reference image will from this time be going to this *.ref file.
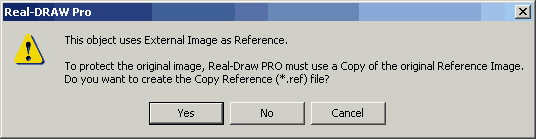
Tip: When you going to paint over the new copy reference image, you will see that it will open in the bitmap editor in its full size. You can now retouch or paint in a very fine detail.
Note: Creating the Ref file will make the current image crop permanent. You can still call Re-Crop tool but you will be able to crop only inside of the previous crop.
Here is an example of Photo Collage
This example will show you the difference in printable output and also show you how to change the Image mode after the import using Re-Crop.
We designed this little postcard using many large mega-pixel images. However to make our point clear with this example, we designed it as a small 400x300 document. As it is, it would be great for web but definitely not for print. This was a breeze because small size makes it easy to handle.

For this image we imported all the photos (photos of paintings) as Normal Object.

Then when all was set up nicely on the canvas, we used the famous Real-Draw Megarender Export to create output 5x the size of 2000x1500

This was Output 1.
After that we selected first image right-click on it and from menu selected Re-Crop.
Tip: Re-Crop not only allows us to change the image crop later (which we don't want to do now) but also change the Image mode.
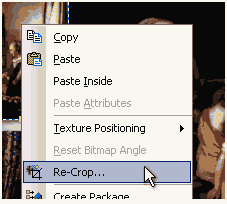
In the old familiar Resize & Crop Window we simply changed the Image mode to Draft Object

We did this for every image on our tiny canvas.
Again, we exported it using 5x Megarender to Output 2.
We can't show you the full result images here, but as you may already know the Output 1 was simply not much better than enlarging the 400x300 collage in a bitmap editor. It wasn't print worthy any more than the original canvas. Just bigger and blurry.
But when we used our images in the Draft with External Reference mode for the Output 2, the result was a large sharp Collage with all the new details taken from original images.
Here is a small crop from the small corner of our 400x300 image after the 5x Megarender . It is obvious which one was using Normal Images and which was using Reference images.

Final thought
The Draft with Reference is an amazing tool to work with many large photos very comfortably on the canvas without thinking too much about the actual sizes. Then we can Megarender it into any size of image and it will automatically use the best resolution possible.